

The application of DTI in the spinal cord is technically limited by the small cross-sectional size of the spinal cord, cerebral spinal fluid pulsation (CSF), the presence of nearby vascular and osseous structures, respiratory and cardiac motion.ĭespite these challenges, studies have successfully reported diffusion measures in the intact human spinal cord. Cronbach’s alpha showed moderate-high values for raters and ROI methods.ĬONCLUSION: The study showed that high reproducibility in spinal cord DTI can be achieved, and demonstrated the importance of setting detailed methodology for post-processing DTI data, specifically the placement of ROIs.ĭiffusion tensor imaging (DTI) has become an important technique for evaluating the central nervous system noninvasively.

FA showed highest variability in ICC values (0.10-0.87). However, no significant differences were observed in DTI parameter values. There were significant differences between raters in the number of pixels selected using free-hand ROIs ( P < 0.05). RESULTS: Inter- and intra-rater agreement between the two ROI methods showed moderate (ICC = 0.5) to strong (ICC = 0.84).
Agreement analyses for fractional anisotropy (FA), axial diffusivity, radial diffusivity and mean diffusivity were performed using intra-class-correlation (ICC) and Cronbach’s alpha statistical methods.

ROIs were placed on axial B 0 maps along the cervical spine using free-hand and fixed-size ROIs. ROIs were drawn by two neuroradiologists on each subject data twice within a 3-mo interval. METHODS: Inner-Field-of-View DTI data previously acquired from ten pediatric healthy subjects (mean age = 12.10 years) was used to assess for reliability. In this study we investigated whether Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI) could be used to assess recovery in patients with mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI).AIM: To assess inter- and intra-rater reliability (agreement) between two region of interest (ROI) methods in pediatric spinal cord diffusion tensor imaging (DTI). You are resurrecting an old thread from 2016 that is not up to date anymore. Thirteen acute mTBI patients 18-50 years of age and seven age- and sex-matched controls with no head injury were recruited from the emergency department of Huntington Memorial Hospital in Pasadena, CA. the scarcity of adequate training data and how big data could be implemented in medical domain is still implicit as on date. Since Orthanc 1.5.0, the DicomModalitiesInDatabase configuration option can be. Images were acquired on three different visits, two weeks and four weeks, respectively, after the first recording, using a 3.0 T.
#Medinria update software#
Image distortions, resulting from susceptibility-induced and by eddy current-induced off-resonance fields, were corrected using routines from the software package FSL.
#Medinria update registration#
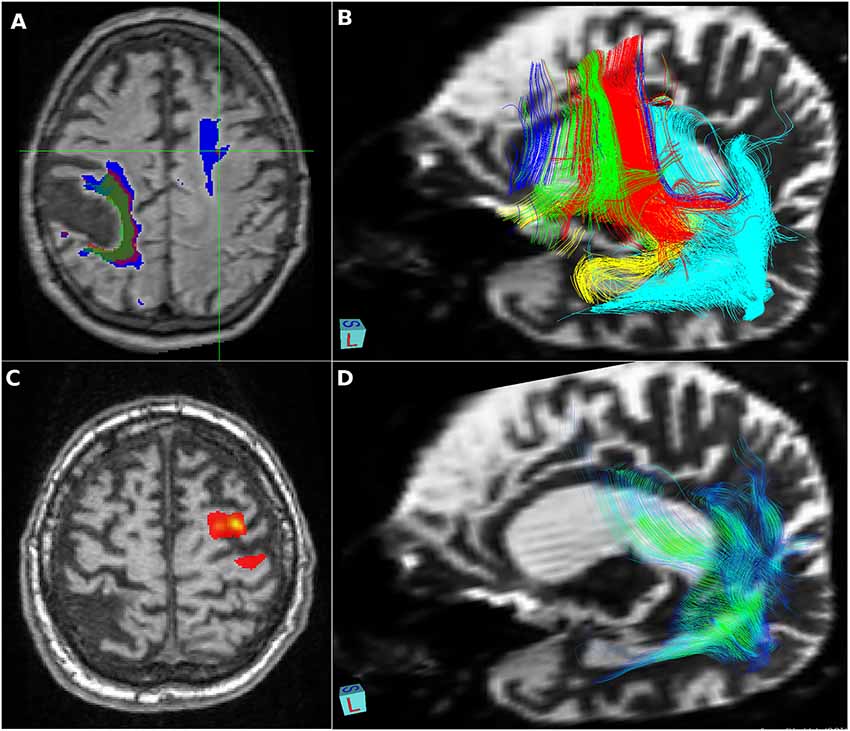
MEDINRIA DATE REGISTRATIONĪn affine linear registration routine part of FSL was also used to align the 32 images to the reference image.įor each DTI dataset, diffusion Fractional Anisotropy (FA), Mean Diffusivity (MD) or Apparent Diffusion Coefficient (ADC), and probabilistic tractography were estimated using FSL and the software package MedInria, with an FA threshold of 200, a minimum length for the detected fibers of 20 mm, and volume sampling every 5 voxels. To perform a quantitative analysis across the two groups, we first used the Johns Hopkins University tractography atlas to define 20 regions of interest (ROI), and the scans from the control subjects to create a reference database that included the mean and standard deviation values in each ROI.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
